Sharks, scientists and tech innovators team up – Blue Carbon Project in action
R-evolution has joined forces with Beneath The Waves to explore and ultimately scale the potential of the world’s biggest nature-based carbon sink: seagrass meadows.
Following successful validation of Beneath The Waves’ initial research, the Bahamian Government is preparing to issue blue carbon credits that are the first of their kind, with Beneath The Waves as the end-to-end science partner and R-evolution as the supplier of multi-dimensional intelligent mapping service for seagrass mapping.
.ashx?la=en&hash=034F622B3DA41E9D1FA65BE050C1E760)
Seagrass is an important part of the coastal biodiversity ecosystem, providing a habitat for small fish and a food source for migratory birds. As a blue carbon ecosystem, seagrass meadows are also crucial to solving environmental challenges, yet they remain among the least recognised and least protected ecological habitats. Blue carbon ecosystems refer to coastal and marine vegetated habitats, such as seagrass meadows, salt marshes and mangrove forests, that naturally sequester and store carbon. Blue carbon ecosystems sequester greenhouse gases approximately thirty-five times faster than tropical rainforests and can store ten to fifteen times as much carbon as their terrestrial counterparts. And, since most carbon is stored in soil and sediments, it can remain there for millennia if left undisturbed.
The Bahamas seagrass meadows are estimated to be up to 92,000 square kilometres – 40% of the world’s known seagrass habitat, storing hundreds of millions of tons of CO2 according to Beneath The Waves’s research.
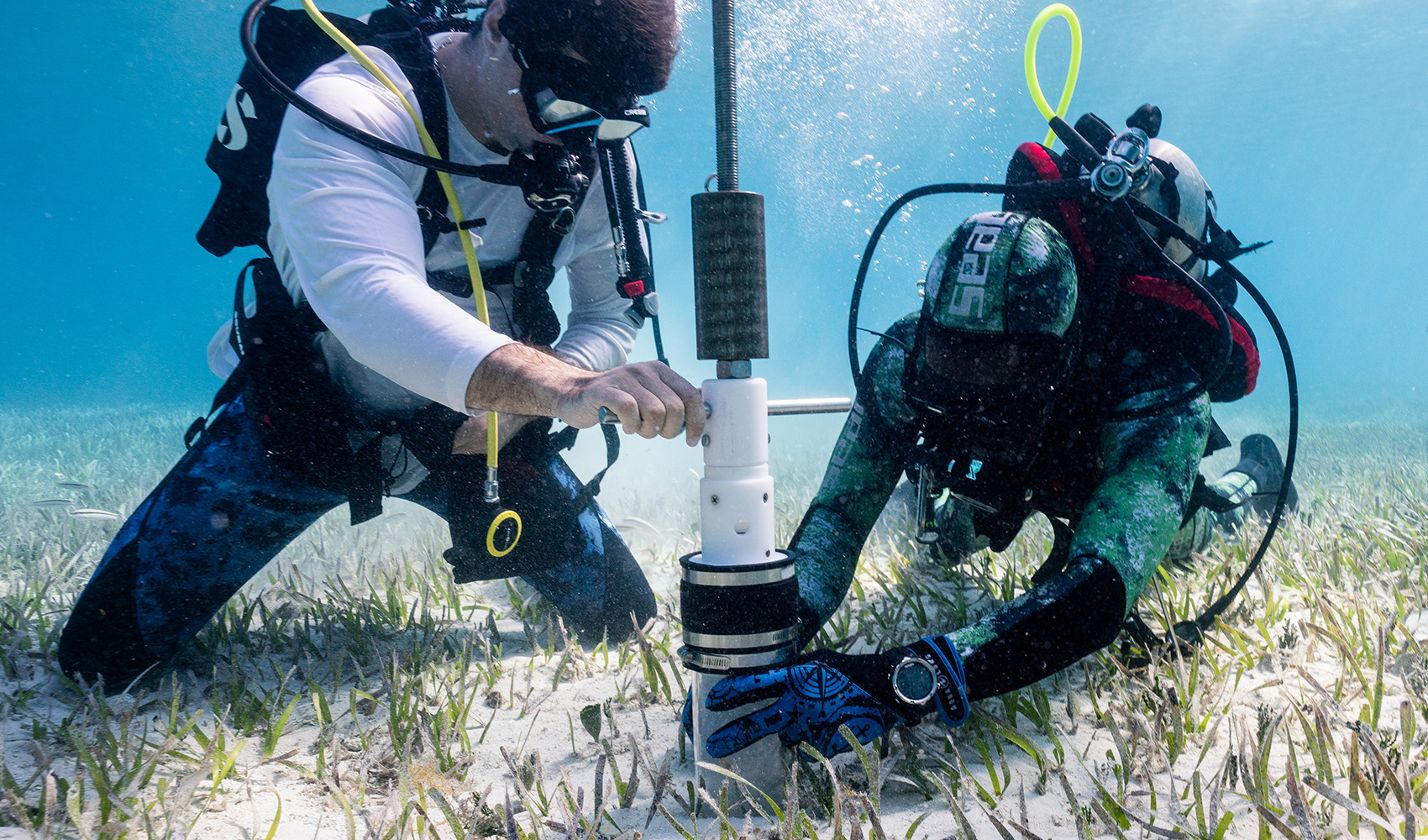
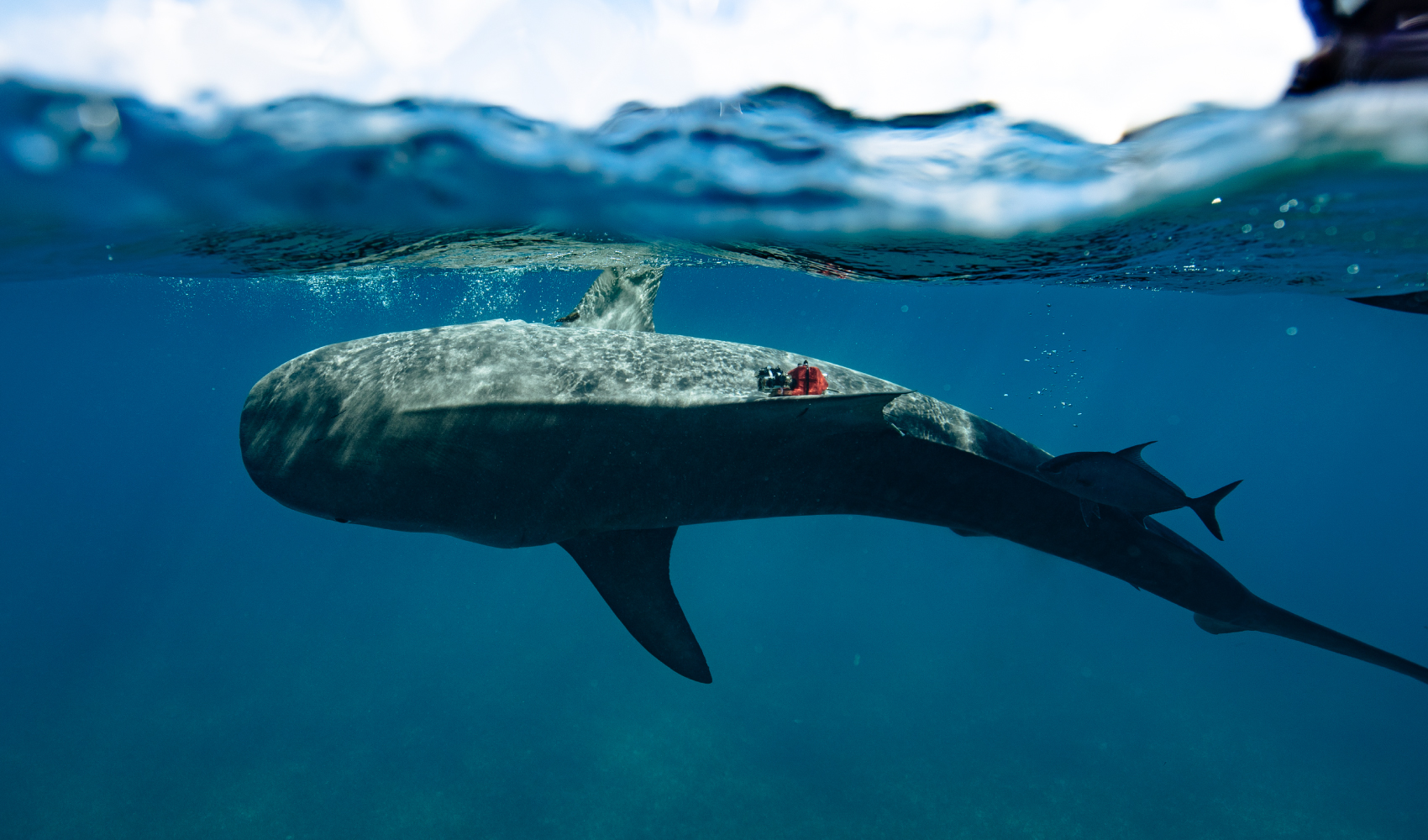


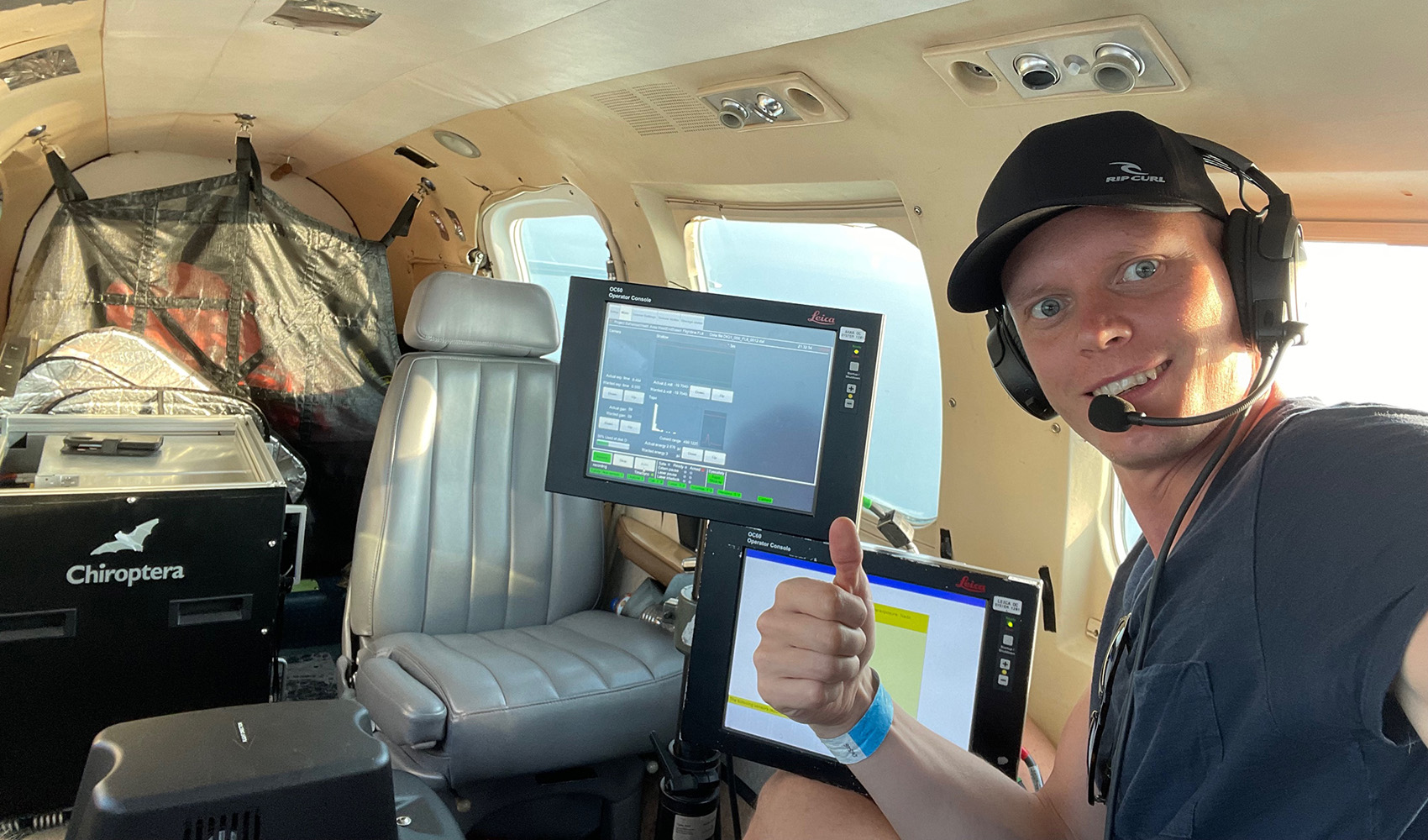
R-evolution’s first blue carbon-related project began in 2021 with Beneath The Waves as our partner. Together we collaborated to map the sprawling seagrass meadows on The Bahama Banks using combined data from sensor-tagged tiger sharks, satellite technology, marine vessel surveys, scuba divers and Hexagon’s airborne bathymetric LiDAR. Current measurement techniques by satellite and boats are not accurate or efficient enough to validate wide areas of seagrass. Utilising Beneath The Waves’ science and aqua experience and Hexagon’s world-leading bathymetric LiDAR, we can play an essential role in supporting, preserving and unlocking the power of nature to build climate resilience.
R-evolution’s deployment of survey aircraft geared with one of Hexagon’s airborne bathymetric LiDAR solutions, the Leica Chiroptera 4X, enables cost-effective, rapid survey of large areas. Compared to current satellite- and vessel-based mapping solutions, airborne bathymetry provides more detailed maps at a faster pace and across larger areas—accurately mapping thousands of square kilometres of seabed habitats at up to 30 metres water depth in just a few days.
Bathymetric surveying supports environmental monitoring by mapping and classifying submerged vegetation and habitat to assess aquacultures, study marine ecology and hydrodynamics.
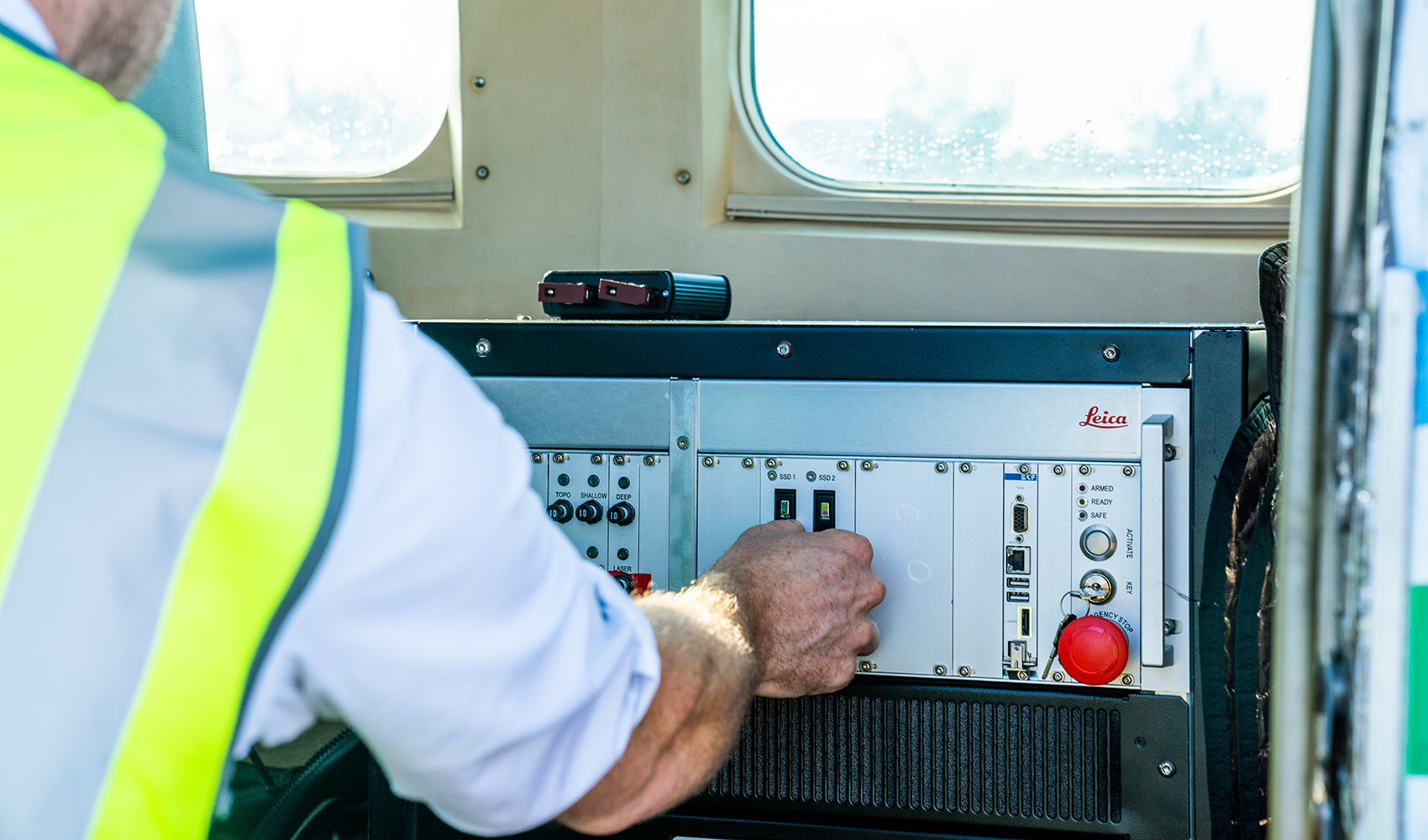


Why use airborne bathymetric LiDAR?
- Seagrass for carbon sequestration is hampered by a lack of accurate measurement.
- Mapping of large areas with vessels, divers and sharks is a long and resource-heavy process.
- Airborne survey can improve the efficiency, resolution and accuracy of the survey while covering the same area in just a few days, offering a more time- and cost-effective solution.
- Bathymetric LiDAR mapping is easily repeatable, offering an excellent basis for year-on-year change detection and monitoring.
- LiDAR point clouds provide 3D elevation and land classification information with higher. positional accuracy and spatial resolutions compared to the 2D coverage of satellite data.
- Airborne bathymetry systems are optimised for shallow water data collection, which makes them ideal for mapping seagrass, which grows primarily in water depths of 30 metres or less.
- The unique combination of bathymetric LiDAR point cloud and AI/ML enables multi-dimensional intelligent mapping of the seabed.

R-evolution will continue the key role in advancing these efforts to mitigate climate damage while protecting the global economy. This mapping is vital to the protection of seagrass habitat across The Bahamas Banks and providing the foundation for a sovereign blue carbon exchange. We are focused on reinventing how industry addresses complex environmental challenges, profitably, using Hexagon’s digital reality solutions.
Learn more about R-evolution’s ocean project helping to protect blue carbon ecosystems below: